Lemur is type of small primate that can be found only on the island of Madagascar. There are 5 families of lemur with more than 50 species and hundreds of subspecies.


Baboons can communicate using more than 30 distinct vocalisations.
Baboon is a type of monkey that can be found in Africa and Arabia. There are five species of baboons. They can survive in different habitats: tropical rainforests, savannas, open woodlands and semi-arid areas.
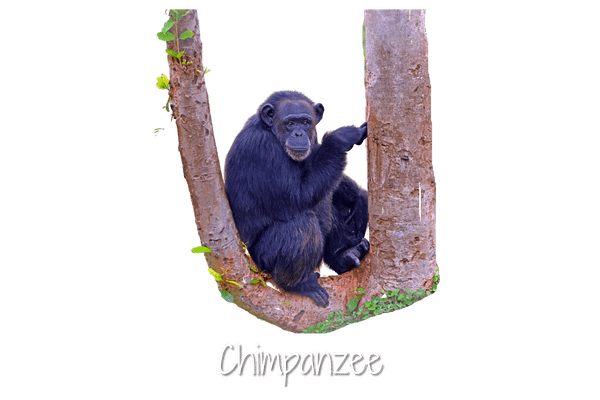
Chimpanzees are apes and they are the closest relatives to humans. They are mammals and have thumbs and fingernails like us. They can stand and walk upright as well.

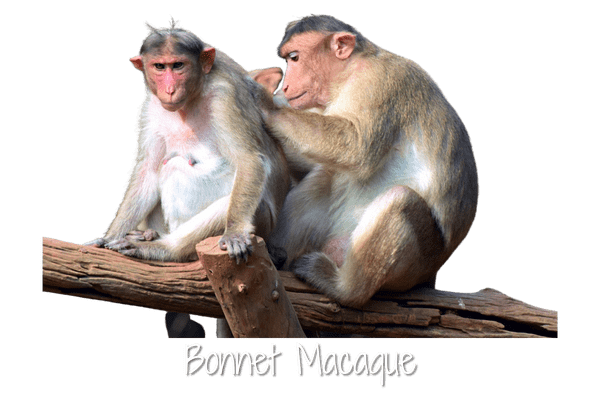
Bonnet macaques likely play a role in tree propagation by dispersing seeds throughout the forest floor.
Bonnet macaque is a species of monkey that belongs to the group of Old World monkeys. There are two subspecies of bonnet macaque that can be found in the southern parts of India.
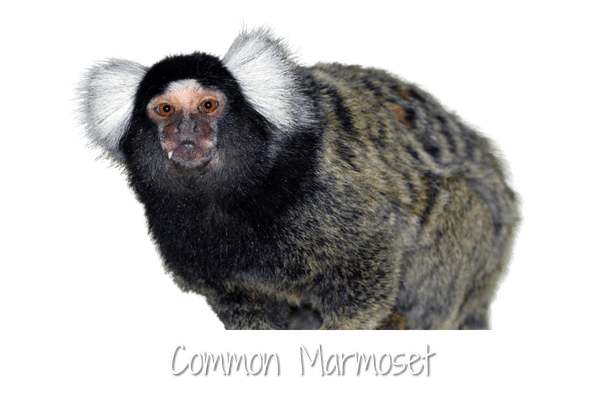
The Common Marmoset is also known as the White-tufted-ear Marmoset or Cotton-eared Marmoset; it has a white blaze on the forehead and white ear tufts.


Stump-tailed macaque babies are born white, and as stump-tailed macaques age, they often begin to lose their hair, males and females alike. Their light pink faces darken to red with age, and often they develop dark blotchy marks on their skin.
Stump-tailed macaques have long, thick, dark brown fur that covers their body, except for face and their short almost invisible tail. Infants are born white and darken as they mature.
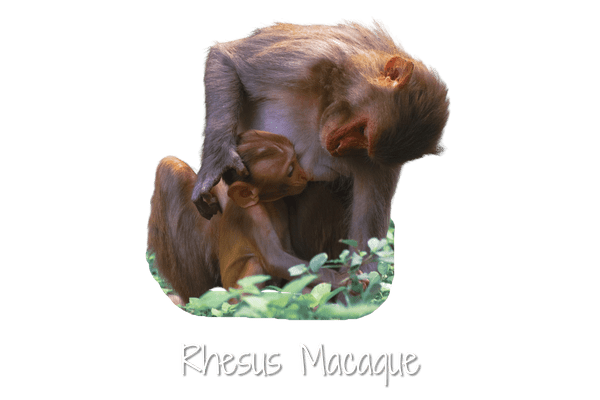
Rhesus macaques are familiar brown primates with red faces and rears. They have close-cropped hair on their heads, which accentuates their very expressive faces.
in IUCN.